| Oracle® Database Object-Relational Developer's Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E11822-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Object-Relational Developer's Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E11822-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter shows how to write object-oriented applications without changing the underlying structure of your relational data.
The chapter contains these topics:
Just as a view is a virtual table, an object view is a virtual object table. Each row in the view is an object: you can call its methods, access its attributes using the dot notation, and create a REF that points to it.
You can run object-oriented applications without converting existing tables to a different physical structure. To do this, you can use object views to prototype or transition to object-oriented applications because the data in the view can be taken from relational tables and accessed as if the table were defined as an object table.
Object views can be used like relational views to present only the data that you want users to see. For example, you might create an object view that presents selected data from an employee table but omits sensitive data about salaries.
Using object views can lead to better performance. Relational data that makes up a row of an object view traverses the network as a unit, potentially saving many round trips.
You can fetch relational data into the client-side object cache and map it into C structures or C++ or Java classes, so 3GL applications can manipulate it just like native classes. You can also use object-oriented features like complex object retrieval with relational data.
You can query the data in new ways by synthesizing objects from relational data. You can view data from multiple tables by using object dereferencing instead of writing complex joins with multiple tables.
You can pin the object data from object views and use the data in the client side object cache. When you retrieve these synthesized objects in the object cache by means of specialized object-retrieval mechanisms, you reduce network traffic.
You gain great flexibility when you create an object model within a view, enabling you to continue developing the model. If you need to alter an object type, you can simply replace the invalidated views with a new definition.
You do not place any restrictions on the characteristics of the underlying storage mechanisms by using objects in views. By the same token, you are not limited by the restrictions of current technology. For example, you can synthesize objects from relational tables which are parallelized and partitioned.
You can create different complex data models from the same underlying data.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for a complete description of SQL syntax and usage.
Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference for a complete discussion of PL/SQL capabilities
Oracle Database Java Developer's Guide for a complete discussion of Java.
Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for a complete discussion of those facilities.
The procedure for defining an object view is:
Define an object type, where each attribute of the type corresponds to an existing column in a relational table.
Write a query that specifies how to extract the data from the relational table. Specify the columns in the same order as the attributes in the object type.
Specify a unique value, based on attributes of the underlying data, to serve as an object identifier, enabling you to create pointers (REFs) to the objects in the view. You can often use an existing primary key.
To update an object view where the attributes of the object type do not correspond exactly to columns in existing tables, you may need to do the following:
Write an INSTEAD OF trigger procedure for Oracle to execute whenever an application program tries to update data in the object view. See "Updating Object Views".
After these steps, you can use an object view just like an object table.
Example 6-1 contains SQL statements to define an object view, where each row in the view is an object of type employee_t:
Example 6-1 Creating an Object View
CREATE TABLE emp_table (
empnum NUMBER (5),
ename VARCHAR2 (20),
salary NUMBER (9,2),
job VARCHAR2 (20));
CREATE TYPE employee_t AS OBJECT (
empno NUMBER (5),
ename VARCHAR2 (20),
salary NUMBER (9,2),
job VARCHAR2 (20));
/
CREATE VIEW emp_view1 OF employee_t
WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER (empno) AS
SELECT e.empnum, e.ename, e.salary, e.job
FROM emp_table e
WHERE job = 'Developer';
insert into emp_table values(1,'John',1000.00,'Architect');
insert into emp_table values(2,'Robert',900.00,'Developer');
insert into emp_table values(3,'James',2000.00,'Director');
select * from emp_view1;
EMPNO ENAME SALARY JOB
---------- -------------------- ---------- --------------------
2 Robert 900 Developer
To access the data from the empnum column of the relational table, access the empno attribute of the object type.
Data in the rows of an object view may come from more than one table, but the object view still traverses the network in one operation. The instance appears in the client side object cache as a C or C++ structure or as a PL/SQL object variable. You can manipulate it like any other native structure.
You can refer to object views in SQL statements in the same way you refer to an object table. For example, object views can appear in a SELECT list, in an UPDATE-SET clause, or in a WHERE clause.
You can also define object views on object views.
You can access object view data on the client side using the same OCI calls you use for objects from object tables. For example, you can use OCIObjectPin() for pinning a REF and OCIObjectFlush() for flushing an object to the server. When you update or flush an object to the database in an object view, the database updates the object view.
See Also:
See Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for more information about OCI calls.An object type can have other object types nested in it as attributes.
If the object type on which an object view is based has an attribute that itself is an object type, then you must provide column objects for this attribute as part of the process of creating the object view. If column objects of the attribute type already exist in a relational table, you can simply select them; otherwise, you must synthesize the object instances from underlying relational data just as you synthesize the principal object instances of the view. You synthesize, or create, these objects by calling the respective constructor methods of the object type to create the object instances, and you can populate their attributes with data from relational columns specified in the constructor.
For example, consider the department table dept in Example 6-2. You might want to create an object view where the addresses are objects inside the department objects. That would allow you to define reusable methods for address objects, and use them for all kinds of addresses.
First, create the types for the address and department objects, then create the view containing the department number, name and address. The address objects are constructed from columns of the relational table.
Example 6-2 Creating a View with Nested Object Types
CREATE TABLE dept (
deptno NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
deptname VARCHAR2(20),
deptstreet VARCHAR2(20),
deptcity VARCHAR2(10),
deptstate CHAR(2),
deptzip VARCHAR2(10));
CREATE TYPE address_t AS OBJECT (
street VARCHAR2(20),
city VARCHAR2(10),
state CHAR(2),
zip VARCHAR2(10));
/
CREATE TYPE dept_t AS OBJECT (
deptno NUMBER,
deptname VARCHAR2(20),
address address_t );
/
CREATE VIEW dept_view OF dept_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER (deptno) AS
SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
address_t(d.deptstreet,d.deptcity,d.deptstate,d.deptzip) AS
deptaddr
FROM dept d;
insert into dept values(1,'Sales','500 Oracle pkwy','Redwood S','CA','94065');
insert into dept values(2,'ST','400 Oracle Pkwy','Redwood S','CA','94065');
insert into dept values(3,'Apps','300 Oracle pkwy','Redwood S','CA','94065');
select * from dept_view;
DEPTNO DEPTNAME
---------- --------------------
ADDRESS(STREET, CITY, STATE, ZIP)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Sales
ADDRESS_T('500 Oracle pkwy', 'Redwood S', 'CA', '94065')
2 ST
ADDRESS_T('400 Oracle Pkwy', 'Redwood S', 'CA', '94065')
3 Apps
ADDRESS_T('300 Oracle pkwy', 'Redwood S', 'CA', '94065')
Because the constructor for an object never returns a null, none of the address objects in the preceding view can ever be null, even if the city, street, and so on columns in the relational table are all null. The relational table has no column that specifies whether or not the department address is null.
By using the DECODE function, or some other function, to return either a null or the constructed object, the null deptstreet column can be used to indicate that the whole address is null.
Example 6-3 Identifying Null Objects in an Object View
-- Requires Ex. 6-2
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW dept_view AS
SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
DECODE(d.deptstreet, NULL, NULL,
address_t(d.deptstreet, d.deptcity, d.deptstate, d.deptzip)) AS deptaddr
FROM dept d;
This technique makes it impossible to directly update the department address through the view, because it does not correspond directly to a column in the relational table. Instead, define an INSTEAD OF trigger over the view to handle updates to this column.
Collections, both nested tables and VARRAYs, can be columns in views. You can select these collections from underlying collection columns or you can synthesize them using subqueries. The CAST-MULTISET operator provides a way of synthesizing such collections.
This section contains the following topics:
Using Example 6-1 and Example 6-2 as starting points, each employee in an emp relational table has the structure in Example 6-4. Using this relational table, you can construct a dept_view with the department number, name, address and a collection of employees belonging to the department.
First, define a nested table type for the employee type employee_t. Next, define a department type with a department number, name, address, and a nested table of employees. Finally, define the object view dept_view.
Example 6-4 Creating a View with a Single-Level Collection
-- Requires Ex. 6-1 and Ex. 6-2
CREATE TABLE emp (
empno NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
empname VARCHAR2(20),
salary NUMBER,
job VARCHAR2 (20),
deptno NUMBER REFERENCES dept(deptno));
CREATE TYPE employee_list_t AS TABLE OF employee_t; -- nested table
/
CREATE TYPE dept_t AS OBJECT (
deptno NUMBER,
deptname VARCHAR2(20),
address address_t,
emp_list employee_list_t);
/
CREATE VIEW dept_view OF dept_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER (deptno) AS
SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
address_t(d.deptstreet,d.deptcity,d.deptstate,d.deptzip) AS deptaddr,
CAST( MULTISET (
SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary, e.job
FROM emp e
WHERE e.deptno = d.deptno)
AS employee_list_t)
AS emp_list
FROM dept d;
insert into dept values(100,'ST','400 Oracle Pkwy','Redwood S','CA',94065);
insert into dept values(200,'Sales','500 Oracle Pkwy','Redwood S','CA',94065);
insert into emp values(1,'John',900,'Developer1',100);
insert into emp values(2,'Robert',1000,'Developer2',100);
insert into emp values(3,'Mary', 1000,'Apps1',200);
insert into emp values(4,'Maria',1500,'Developer3',200);
select * from dept_view where deptno = 100;
DEPTNO DEPTNAME
---------- --------------------
ADDRESS(STREET, CITY, STATE, ZIP)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EMP_LIST(EMPNO, ENAME, SALARY, JOB)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 ST
ADDRESS_T('400 Oracle Pkwy', 'Redwood S', 'CA', '94065')
EMPLOYEE_LIST_T(EMPLOYEE_T(1, 'John', 900, 'Developer1'), EMPLOYEE_T(2, 'Robert'
, 1000, 'Developer2'))
select emp_list from dept_view where deptno = 100;
EMP_LIST(EMPNO, ENAME, SALARY, JOB)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EMPLOYEE_LIST_T(EMPLOYEE_T(1, 'John', 900, 'Developer1'), EMPLOYEE_T(2, 'Robert'
, 1000, 'Developer2'))
The SELECT subquery inside the CAST-MULTISET block selects the list of employees that belong to the current department. The MULTISET keyword indicates that this is a list as opposed to a singleton value. The CAST operator casts the result set into the appropriate type, in this case to the employee_list_t nested table type.
A query on this view could provide the list of departments, with each department row containing the department number, name, the address object and a collection of employees belonging to the department.
Multilevel collections and single-level collections are created and used in object views in the same way. The only difference is that, for a multilevel collection, you must create an additional level of collections.
Example 6-5 builds an object view containing a multilevel collection. The view is based on flat relational tables that contain no collections. As a preliminary to building the object view, the example creates the object and collection types it uses. An object type (for example, emp_t) is defined to correspond to each relational table, with attributes whose types correspond to the types of the respective table columns. In addition, the employee type has a nested table (attribute) of projects, and the department type has a nested table (attribute) of employees. The latter nested table is a multilevel collection. The CAST-MULTISET operator is used in the CREATE VIEW statement to build the collections.
Example 6-5 Creating a View with Multilevel Collections
CREATE TABLE depts
( deptno NUMBER,
deptname VARCHAR2(20));
CREATE TABLE emps
( ename VARCHAR2(20),
salary NUMBER,
deptname VARCHAR2(20));
CREATE TABLE projects
( projname VARCHAR2(20),
mgr VARCHAR2(20));
CREATE TYPE project_t AS OBJECT
( projname VARCHAR2(20),
mgr VARCHAR2(20));
/
CREATE TYPE nt_project_t AS TABLE OF project_t;
/
CREATE TYPE emp_t AS OBJECT
( ename VARCHAR2(20),
salary NUMBER,
deptname VARCHAR2(20),
projects nt_project_t );
/
CREATE TYPE nt_emp_t AS TABLE OF emp_t;
/
CREATE TYPE depts_t AS OBJECT
( deptno NUMBER,
deptname VARCHAR2(20),
emps nt_emp_t );
/
CREATE VIEW v_depts OF depts_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER (deptno) AS
SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
CAST(MULTISET(SELECT e.ename, e.salary, e.deptname,
CAST(MULTISET(SELECT p.projname, p.mgr
FROM projects p
WHERE p.mgr = e.ename)
AS nt_project_t)
FROM emps e
WHERE e.deptname = d.deptname)
AS nt_emp_t)
FROM depts d;
You can construct pointers (REFs) to the row objects in an object view. Because the view data is not stored persistently, you must specify a set of distinct values to be used as object identifiers. Object identifiers allow you to reference the objects in object views and pin them in the object cache.
If the view is based on an object table or an object view, then there is already an object identifier associated with each row and you can reuse them. To do this, either omit the WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER clause or specify WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER DEFAULT.
However, if the row object is synthesized from relational data, you must choose some other set of values.
You can specify object identifiers based on the primary key. This turns the set of unique keys that identify the row object into an identifier for the object. These values must be unique within the rows selected out of the view, because duplicates would lead to problems during navigation through object references.
See Also:
"Using Object Identifiers to Identify Row Objects" for a description of primary-key based and system-generated object identifiersObject views created with the WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER Clause
An object view created with the WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER clause has an object identifier derived from the primary key.
For example, note the definition of the object type dept_t and the object view dept_view described in "Single-Level Collections in Object Views".
Because the underlying relational table has deptno as the primary key, each department row has a unique department number. In the view, the deptno column becomes the deptno attribute of the object type. Once you know that deptno is unique within the view objects, you can specify it as the object identifier.
Object views created with the WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER DEFAULT Clause
If the WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER DEFAULT clause is specified, the object identifier is either system-generated or primary-key based, depending on the underlying table or view definition.
See Also:
See "Storage Considerations for Object Identifiers (OIDs)".In this connected group of examples, Example 6-2 and Example 6-4, each object selected out of the dept_view view has a unique object identifier derived from the department number value. In the relational case, the foreign key deptno in the emp employee table matches the deptno primary key value in the dept department table. The primary key value creates the object identifier in the dept_view, allowing the foreign key value in the emp_view to create a reference to the primary key value in dept_view.
To synthesize a primary key object reference, use the MAKE_REF operator. This takes the view or table name that the reference points to, and a list of foreign key values, to create the object identifier portion of the reference that matches a specific object in the referenced view.
Example 6-6 creates an emp_view view which has the employee's number, name, salary and a reference to the employee's department, by first creating the employee type emp_t and then the view based on that type.
Example 6-6 Creating a Reference to Objects in a View
-- Requires Ex. 6-2 and Ex. 6-4
-- if you have previously created emp_t, you must drop it
CREATE TYPE emp_t AS OBJECT (
empno NUMBER,
ename VARCHAR2(20),
salary NUMBER,
deptref REF dept_t);
/
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW emp_view OF emp_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(empno)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary,
MAKE_REF(dept_view, e.deptno)
FROM emp e;
The deptref column in the view holds the department reference. The following simple query retrieves all employees whose departments are located in the city of Redwood S:
SELECT e.empno, e.salary, e.deptref.deptno
FROM emp_view e
WHERE e.deptref.address.city = 'Redwood S';
EMPNO SALARY DEPTREF.DEPTNO
---------- ---------- --------------
2 1000 100
1 900 100
4 1500 200
3 1000 200
Note that you can also create emp_view using the REF modifier instead of MAKE_REF as follows to get the reference to the dept_view objects:
Example 6-7 Query References to Objects with REF
-- Requires Ex. 6-2, Ex. 6-4, and Ex. 6-6
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW emp_view OF emp_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(empno)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary, REF(d)
FROM emp e, dept_view d
WHERE e.deptno = d.deptno;
In Example 6-7, the dept_view joins the emp table on the deptno key.
The advantage of using the MAKE_REF operator, as in Example 6-6, instead of the REF modifier is that with the former, you can create circular references. For example, you can create an employee view that has a reference to the employee's department, while the department view has a list of references to the employees who work in that department.
Note that if the object view has a primary-key based object identifier, the reference to such a view is primary-key based. On the other hand, a reference to a view with system-generated object identifier is a system-generated object reference. This difference is only relevant when you create object instances in the OCI object cache and need to get the reference to the newly created objects.
See Also:
"Object Cache"As with synthesized objects, you can also select persistently stored references as view columns and use them seamlessly in queries. However, the object references to view objects cannot be stored persistently.
You can use views with objects to model inverse relationships.
One-to-one relationships can be modeled with inverse object references. For example, suppose that each employee has a particular desktop computer, and that the computer belongs to that employee only. A relational model would capture this using foreign keys either from the computer table to the employee table, or in the reverse direction. Using views, you can model the objects so there is an object reference from the employee to the computer object and also a reference from the computer object to the employee.
One-to-Many and Many-to-One Relationships
One-to-many relationships (or many-to-many relationships) can be modeled either by using object references or by embedding the objects. One-to-many relationship can be modeled by having a collection of objects or object references. The many-to-one side of the relationship can be modeled using object references.
Consider the department-employee case. In the underlying relational model, the foreign key is in the employee table. The relationship between departments and employees can be modeled using collections in views. The department view can have a collection of employees, and the employee view can have a reference to the department (or inline the department values). This gives both the forward relation (from employee to department) and the inverse relation (department to list of employees). The department view can also have a collection of references to employee objects instead of embedding the employee objects.
You can update, insert, and delete data in an object view using the same SQL DML you use for object tables. Oracle updates the base tables of the object view if there is no ambiguity.
Views are not always directly updatable.
A view is not directly updatable if the view query contains joins, set operators, aggregate functions, or GROUP BY or DISTINCT clauses. Also, individual columns of a view are not directly updatable if they are based on pseudocolumns or expressions in the view query.
If a view is not directly updatable, you can still update it indirectly using INSTEAD OF triggers. To do so, you define an INSTEAD OF trigger for each kind of DML statement you want to execute on the view. In the INSTEAD OF trigger, code the operations that must take place on the underlying tables of the view to accomplish the desired change in the view. Then, when you issue a DML statement for which you have defined an INSTEAD OF trigger, Oracle transparently runs the associated trigger.
See Also:
"Using INSTEAD OF Triggers to Control Mutating and Validation" for an example of anINSTEAD OF triggerNote:
In an object view hierarchy,UPDATE and DELETE statements operate polymorphically just as SELECT statements do: the set of rows picked out by an UPDATE or DELETE statement on a view implicitly includes qualifying rows in any subviews of the specified view as well.For example, the following statement, which deletes all persons from Person_v, also deletes all students from Student_v and all employees from the Employee_v view.
DELETE FROM Person_v;
To exclude subviews and restrict the affected rows to just those in the view specified, use the ONLY keyword. For example, the following statement updates only persons and not employees or students.
UPDATE ONLY(Person_v) SET address = ...
See Also:
"Object View Hierarchies" for a discussion of object view hierarchy and examples definingStudent_v and Employee_v viewsYou can modify a nested table by inserting new elements and updating or deleting existing elements. Nested table columns that are virtual or synthesized, as in a view, are not usually updatable. To overcome this, Oracle allows INSTEAD OF triggers to be created on these columns.
The INSTEAD OF trigger defined on a nested table column (of a view) is fired when the column is modified. Note that if the entire collection is replaced (by an update of the parent row), the INSTEAD OF trigger on the nested table column is not fired.
INSTEAD OF triggers provide a way to update complex views that otherwise could not be updated. They can also be used to enforce constraints, check privileges, and validate DML statements. Using these triggers, you can control mutation that might be caused by inserting, updating, and deleting in the objects created though an object view.
For instance, to enforce the condition that the number of employees in a department cannot exceed 10, you can write an INSTEAD OF trigger for the employee view. The trigger is not needed to execute the DML statement because the view can be updated, but you need it to enforce the constraint.
Example 6-8 shows how to implement the trigger by means of SQL statements.
Example 6-8 Creating INSTEAD OF Triggers on a View
-- Requires Ex. 6-2, Ex. 6-4, and Ex. 6-6
CREATE TRIGGER emp_instr INSTEAD OF INSERT on emp_view
FOR EACH ROW
DECLARE
dept_var dept_t;
emp_count integer;
BEGIN
-- Enforce the constraint
-- First get the department number from the reference
UTL_REF.SELECT_OBJECT(:NEW.deptref, dept_var);
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO emp_count
FROM emp
WHERE deptno = dept_var.deptno;
IF emp_count < 9 THEN
-- Do the insert
INSERT INTO emp (empno, empname, salary, deptno)
VALUES (:NEW.empno, :NEW.ename, :NEW.salary, dept_var.deptno);
END IF;
END;
/
See Also:
"Triggers for Object Tables"Although you cannot directly access remote tables as object tables, object views let you access remote tables as if they were object tables.
Consider a company with two branches; one in Washington D.C. and another in Chicago. Each site has an employee table. The headquarters in Washington has a department table with a list of all the departments. To get a total view of the entire organization, you can create views over the individual remote tables and then a overall view of the organization.
To this requires the following:
Update the entry in listener.ora, such as: (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp) (HOST=stadv07.us.example.com)(PORT=1640))
Add entries to tnsnames.ora, such as: chicago=(DESCRIPTION= (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=linux)) (CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=linux.regress.rdbms.dev.us.example.com)))
Provide CREATE DATABASE LINK code as shown in Example 6-9
Example 6-9 begins by creating an object view for each employee table and then creates the global view.
Example 6-9 Creating an Object View to Access Remote Tables
-- Requires Ex. 6-2, Ex. 6-4, and Ex. 6-6
-- Example requires DB links, such as these, modify for your use and uncomment
-- CREATE DATABASE LINK chicago CONNECT TO hr IDENTIFIED BY hr USING 'inst1';
-- CREATE DATABASE LINK washington CONNECT TO hr IDENTIFIED BY hr USING 'inst1';
CREATE VIEW emp_washington_view (eno, ename, salary, job)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary, e.job
FROM emp@washington e;
CREATE VIEW emp_chicago_view (eno, ename, salary, job)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary, e.job
FROM emp@chicago e;
CREATE VIEW orgnzn_view OF dept_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER (deptno)
AS SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
address_t(d.deptstreet,d.deptcity,d.deptstate,d.deptzip) AS deptaddr,
CAST( MULTISET (
SELECT e.eno, e.ename, e.salary, e.job
FROM emp_washington_view e)
AS employee_list_t) AS emp_list
FROM dept d
WHERE d.deptcity = 'Washington'
UNION ALL
SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
address_t(d.deptstreet,d.deptcity,d.deptstate,d.deptzip) AS deptaddr,
CAST( MULTISET (
SELECT e.eno, e.ename, e.salary, e.job
FROM emp_chicago_view e)
AS employee_list_t) AS emp_list
FROM dept d
WHERE d.deptcity = 'Chicago';
This view has a list of all employees for each department. The UNION ALL clause is used because employees cannot work in more than one department.
You can define circular references in object views using the MAKE_REF operator: view_A can refer to view_B which in turn can refer to view_A. This allows an object view to synthesize a complex structure such as a graph from relational data.
For example, in the case of the department and employee, the department object currently includes a list of employees. To conserve space, you may want to put references to the employee objects inside the department object, instead of materializing all the employees within the department object. You can construct (pin) the references to employee objects, and later follow the references using the dot notation to extract employee information.
Because the employee object already has a reference to the department in which the employee works, an object view over this model contains circular references between the department view and the employee view.
You can create circular references between object views in two different ways:
Note:
Both ways to create circular references require the setup described in "Tables and Types to Demonstrate Circular View References".First View After Second View
Create view A without any reference to view B.
Create view B, which includes a reference to view A.
Replace view A with a new definition that includes the reference to view B.
See the example in "Method 1: Re-create First View After Creating Second View"
First View Using the FORCE Keyword
Create view A with a reference to view B using the FORCE keyword.
Create view B with a reference to view A. When view A is used, it is validated and re-compiled.
See the example in "Method 2: Create First View Using FORCE Keyword"
Method 2 has fewer steps, but the FORCE keyword may hide errors in the view creation. You need to query the USER_ERRORS catalog view to see if there were any errors during the view creation. Use this method only if you are sure that there are no errors in the view creation statement.
Also, if errors prevent the views from being recompiled upon use, you must recompile them manually using the ALTER VIEW COMPILE command.
Perform the setup described next before attempting to use either method of creating circular view references.
First, you need set up some relational tables and associated object types. Although the tables contain some objects, they are not object tables. To access the data objects, you will create object views later.
The emp table stores the employee information:
Example 6-10 Creating emp table to demonstrate circular references
CREATE TABLE emp
( empno NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
empname VARCHAR2(20),
salary NUMBER,
deptno NUMBER );
-- first create a dummy, that is, incomplete, department type, so emp_t type
-- created later will succeed
CREATE TYPE dept_t;
/
-- Create the employee type with a reference to the department, dept_t:
CREATE TYPE emp_t AS OBJECT
( eno NUMBER,
ename VARCHAR2(20),
salary NUMBER,
deptref REF dept_t );
/
-- Represent the list of references to employees as a nested table:
CREATE TYPE employee_list_ref_t AS TABLE OF REF emp_t;
/
-- Create the department table as a relational table
CREATE TABLE dept
( deptno NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
deptname VARCHAR2(20),
deptstreet VARCHAR2(20),
deptcity VARCHAR2(10),
deptstate CHAR(2),
deptzip VARCHAR2(10) );
-- Create object types that map to columns from the relational tables:
CREATE TYPE address_t AS OBJECT
( street VARCHAR2(20),
city VARCHAR2(10),
state CHAR(2),
zip VARCHAR2(10));
/
-- Fill in the definition for dept_t, the incomplete type you previously created:
CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE dept_t AS OBJECT
( dno NUMBER,
dname VARCHAR2(20),
deptaddr address_t,
empreflist employee_list_ref_t);
/
As Example 6-10 indicates, you must create the emp table, then create a dummy department type, dept_t which will enable the emp_t type to succeed once you create it. After that, create emp_t with a reference to dept_t. Create a list of references to employees as a nested table, employee_list_ref_t and create the department table, dept. Then create an object type, address_t that has columns mapping to the relational tables, and finally fill in the definition for the incomplete dept_t.
The following is example data you could use:
insert into emp values(1,'John','900',100); insert into emp values(2,'james','1000',100); insert into emp values(3,'jack',2000,200);
Now that you have established the underlying relational table definitions, in the previous section, create the object views on top of them.
Method 1: Re-create First View After Creating Second View
First create the employee view with a null in the deptref column. Later, you can turn that column into a reference.
Next, create the department view, which includes references to the employee objects. This creates a list of references to employee objects, instead of including the entire employee object.
Next, re-create the employee view with the reference to the department view.
Example 6-11 Creating an Object View with a Circular Reference, Method 1
-- Requires Ex. 6-10
CREATE VIEW emp_view OF emp_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(eno)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary, NULL
FROM emp e;
-- create department view, including references to the employee objects
CREATE VIEW dept_view OF dept_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(dno)
AS SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
address_t(d.deptstreet,d.deptcity,d.deptstate,d.deptzip),
CAST( MULTISET (
SELECT MAKE_REF(emp_view, e.empno)
FROM emp e
WHERE e.deptno = d.deptno)
AS employee_list_ref_t)
FROM dept d;
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW emp_view OF emp_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(eno)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary,
MAKE_REF(dept_view, e.deptno)
FROM emp e;
This creates the views.
Method 2: Create First View Using FORCE Keyword
If you are sure that the view creation statement has no syntax errors, you can use the FORCE keyword to force the creation of the first view without the other view being present.
First, create an employee view that includes a reference to the department view, which does not exist at this point. This view cannot be queried until the department view is created properly.
Next, create a department view that includes references to the employee objects. You do not have to use the FORCE keyword here, because emp_view already exists. This allows you to query the department view, getting the employee object by dereferencing the employee reference from the nested table empreflist.
Example 6-12 Creating view with FORCE Method 2
-- Requires Ex. 6-10
-- create employee view
CREATE OR REPLACE FORCE VIEW emp_view OF emp_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(eno)
AS SELECT e.empno, e.empname, e.salary,
MAKE_REF(dept_view, e.deptno)
FROM emp e;
-- create a department view that includes references to the employee objects
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW dept_view OF dept_t WITH OBJECT IDENTIFIER(dno)
AS SELECT d.deptno, d.deptname,
address_t(d.deptstreet,d.deptcity,d.deptstate,d.deptzip),
CAST( MULTISET (
SELECT MAKE_REF(emp_view, e.empno)
FROM emp e
WHERE e.deptno = d.deptno)
AS employee_list_ref_t)
FROM dept d;
-- Querying with DEREF method
SELECT DEREF(e.COLUMN_VALUE)
FROM TABLE( SELECT e.empreflist FROM dept_view e WHERE e.dno = 100) e;
COLUMN_VALUE is a special name that represents the scalar value in a scalar nested table. In this case, COLUMN_VALUE denotes the reference to the employee objects in the nested table empreflist.
You can also access the employee number only, for all those employees whose name begins with John.
Example 6-13 Querying with COLUMN_VALUE
-- Requires Ex. 6-10 and 6-12 SELECT e.COLUMN_VALUE.eno FROM TABLE(SELECT e.empreflist FROM dept_view e WHERE e.dno = 100) e WHERE e.COLUMN_VALUE.ename like 'John%';
To get a tabular output, unnest the list of references by joining the department table with the items in its nested table:
Example 6-14 Querying with COLUMN_VALUE, Unnesting References
-- Requires Ex. 6-10 and 6-12SELECT d.dno, e.COLUMN_VALUE.eno, e.COLUMN_VALUE.ename FROM dept_view d, TABLE(d.empreflist) e WHERE e.COLUMN_VALUE.ename like 'John%' AND d.dno = 100;
Finally, you can rewrite the preceding query to use the emp_view instead of the dept_view to show how to navigate from one view to the other:
An object view hierarchy is a set of object views each of which is based on a different type in a type hierarchy. Subviews in a view hierarchy are created under a superview, analogously to the way subtypes in a type hierarchy are created under a supertype.
Each object view in a view hierarchy is populated with objects of a single type, but queries on a given view implicitly address its subviews as well. Thus an object view hierarchy gives you a simple way to frame queries that can return a polymorphic set of objects of a given level of specialization or greater.
For example, suppose you have the following type hierarchy, with person_typ as the root:
If you have created an object view hierarchy based on this type hierarchy, with an object view built on each type, you can query the object view that corresponds to the level of specialization you are interested in. For instance, you can query the view of student_typ to get a result set that contains only students, including part-time students.
You can base the root view of an object view hierarchy on any type in a type hierarchy: you do not need to start the object view hierarchy at the root type. Nor do you need to extend an object view hierarchy to every leaf of a type hierarchy or cover every branch. However, you cannot skip intervening subtypes in the line of descent. Any subview must be based on a direct subtype of the type of its direct superview.
Just as a type can have multiple sibling subtypes, an object view can have multiple sibling subviews. However, a subview based on a given type can participate in only one object view hierarchy: two different object view hierarchies cannot each have a subview based on the same subtype.
A subview inherits the object identifier (OID) from its superview. An OID cannot be explicitly specified in any subview.
A root view can explicitly specify an object identifier using the WITH OBJECT ID clause. If the OID is system-generated or the clause is not specified in the root view, then subviews can be created only if the root view is based on a table or view that also uses a system-generated OID.
The query underlying a view determines whether or not the view is updatable. For a view to be updatable, its query must contain no joins, set operators, aggregate functions, GROUP BY clause, DISTINCT clause, pseudocolumns, or expressions. The same applies to subviews.
If a view is not updatable, you can define INSTEAD OF triggers to perform appropriate DML actions. Note that INSTEAD OF triggers are not inherited by subviews.
All views in a view hierarchy must be in the same schema.
Note:
You can create views of types that are non-instantiable. A non-instantiable type cannot have instances, so ordinarily there would be no point in creating an object view of such a type. However, a non-instantiable type can have subtypes that are instantiable. The ability to create object views of non-instantiable types enables you to base an object view hierarchy on a type hierarchy that contains a non-instantiable type.You build an object view hierarchy by creating subviews under a root view. You do this by using the UNDER keyword in the CREATE VIEW statement, as show in Example 6-17.
The same object view hierarchy can be based on different underlying storage models. In other words, a variety of layouts or designs of underlying tables can produce the same object view hierarchy. The design of the underlying storage model affects the performance and updatability of the object view hierarchy.
This section describes three possible storage models. In the first, a flat model, all views in the object view hierarchy are based on the same table. In the second, a horizontal model, each view has a one-to-one correspondence with a different table. And in the third, a vertical model, the views are constructed using joins.
To execute any of these storage models, first create types shown in Example 6-16.
Example 6-16 Creating Types for Storage Model Examples
CREATE TYPE person_typ AS OBJECT ( ssn NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(30), address VARCHAR2(100)) NOT FINAL;/ CREATE TYPE student_typ UNDER person_typ ( deptid NUMBER, major VARCHAR2(30)) NOT FINAL;/ CREATE TYPE employee_typ UNDER person_typ ( empid NUMBER, mgr VARCHAR2(30));/
This section contains the following topics:
In the flat model, all the views in the hierarchy are based on the same table. In the following example, the single table AllPersons contains columns for all the attributes of person_typ, student_typ, and employee_typ.
Figure 6-2 Flat Storage Model for Object View Hierarchy
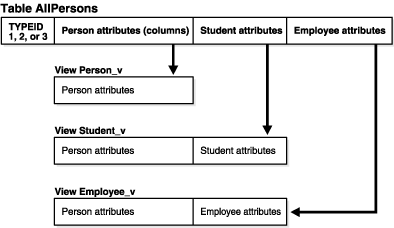
The typeid column identifies the type of each row. These possible values are the types created in Example 6-16, 1 = person_typ, 2 = student_typ, and 3 = employee_typ:
Example 6-17 creates the table AllPersons and then the views that make up the object view hierarchy:
Example 6-17 Creating an Object View Hierarchy
-- Requires Ex. 6-16 CREATE TABLE AllPersons ( typeid NUMBER(1), ssn NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(30), address VARCHAR2(100), deptid NUMBER, major VARCHAR2(30), empid NUMBER, mgr VARCHAR2(30)); CREATE VIEW Person_v OF person_typ WITH OBJECT OID(ssn) AS SELECT ssn, name, address FROM AllPersons WHERE typeid = 1; CREATE VIEW Student_v OF student_typ UNDER Person_v AS SELECT ssn, name, address, deptid, major FROM AllPersons WHERE typeid = 2; CREATE VIEW Employee_v OF employee_typ UNDER Person_v AS SELECT ssn, name, address, empid, mgr FROM AllPersons WHERE typeid = 3;
The flat model has the advantage of simplicity and poses no obstacles to supporting indexes and constraints. Its drawbacks are:
A single table cannot contain more than 1000 columns, so the flat model imposes a 1000-column limit on the total number of columns that the object view hierarchy can contain.
Each row of the table will have NULLs for all the attributes not belonging to its type. Such non-trailing NULLs can adversely affect performance.
On the horizontal model, each view or subview is based on a different table. In the example, the tables are relational, but they could just as well be object tables for which column substitutability is turned off.
Figure 6-3 Horizontal Storage Model for Object View Hierarchy
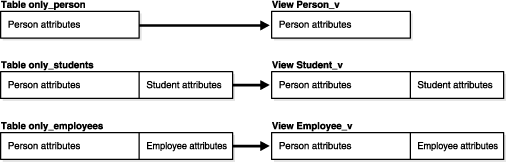
Example 6-18 creates tables and then views based on these tables.
Example 6-18 -- Creating Table Horizontal Model
-- Requires Ex. 6-16 and Ex. 6-17 CREATE TABLE only_persons ( ssn NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(30), address VARCHAR2(100)); CREATE TABLE only_students ( ssn NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(30), address VARCHAR2(100), deptid NUMBER, major VARCHAR2(30)); CREATE TABLE only_employees ( ssn NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(30), address VARCHAR2(100), empid NUMBER, mgr VARCHAR2(30)); CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW Person_v OF person_typ WITH OBJECT OID(ssn) AS SELECT * FROM only_persons; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW Student_v OF student_typ UNDER Person_v AS SELECT * FROM only_students; CREATE OR REPlACE VIEW Employee_v OF employee_typ UNDER Person_v AS SELECT * FROM only_employees;
The horizontal model is very efficient at processing queries of the form:
Example 6-19 -- Querying views horizontal model
-- Requires Ex. 6-16 and Ex. 6-17 -- add the following data insert into only_persons values(1234,'John','abc'); insert into only_students values(1111,'James','abc',100,'CS'); insert into only_employees values(2222,'jack','abc',400,'Juliet'); SELECT VALUE(p) FROM Person_v p WHERE VALUE(p) IS OF (ONLY student_typ); OUTPUT: VALUE(P)(SSN, NAME, ADDRESS) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- STUDENT_TYP(1111, 'James', 'abc', 100, 'CS')
Such queries only need to access a single physical table to get all the objects of the specific type. The drawbacks of this model are that queries such as SELECT * FROM view require performing a UNION over all the underlying tables and projecting the rows over just the columns in the specified view. (See "Querying a View in a Hierarchy".) Also, indexes on attributes (and unique constraints) must span multiple tables, and support for this does not currently exist.
In the vertical model, there is a physical table corresponding to each view in the hierarchy, but the physical tables store only those attributes that are unique to their corresponding subtypes.
Figure 6-4 Vertical Storage Model for Object View Hierarchy
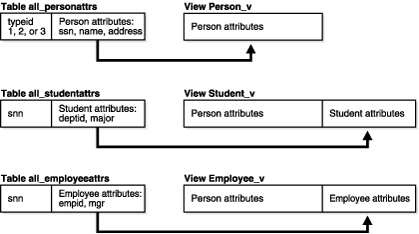
Example 6-20 creates tables and then corresponding views.
Example 6-20 Creating table, views vertical model
CREATE TABLE all_personattrs ( typeid NUMBER, ssn NUMBER, name VARCHAR2(30), address VARCHAR2(100)); CREATE TABLE all_studentattrs ( ssn NUMBER, deptid NUMBER, major VARCHAR2(30)); CREATE TABLE all_employeeattrs ( ssn NUMBER, empid NUMBER, mgr VARCHAR2(30)); CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW Person_v OF person_typ WITH OBJECT OID(ssn) AS SELECT ssn, name, address FROM all_personattrs WHERE typeid = 1; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW Student_v OF student_typ UNDER Person_v AS SELECT x.ssn, x.name, x.address, y.deptid, y.major FROM all_personattrs x, all_studentattrs y WHERE x.typeid = 2 AND x.ssn = y.ssn; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW Employee_v OF employee_typ UNDER Person_v AS SELECT x.ssn, x.name, x.address, y.empid, y.mgr FROM all_personattrs x, all_employeeattrs y WHERE x.typeid = 3 AND x.ssn = y.ssn;
The vertical model can efficiently process queries of the kind SELECT * FROM root_view, and it is possible to index individual attributes and impose unique constraints on them. However, to re-create an instance of a type, a join over object identifiers (OIDs) must be performed for each level that the type is removed from the root in the hierarchy.
You can query any view or subview in an object view hierarchy; rows are returned for the declared type of the view that you query and for any of the subtypes of that type. So, for instance, in an object view hierarchy based on the person_typ type hierarchy, you can query the view of person_typ to get a result set that contains all persons, including students and employees; or you can query the view of student_typ to get a result set that contains only students, including part-time students.
In the SELECT list of a query, you can include either functions such as REF() and VALUE() that return an object instance, or you can specify object attributes of the declared type of the view, such as the name and ssn attributes of person_typ.
If you specify functions, to return object instances, the query returns a polymorphic result set: that is, it returns instances of both the declared type of the view and any subtypes of that type.
For example, the following query returns instances of persons, employees, and students of all types, as well as REFs to those instances.
Example 6-21 Query with REF and Value
-- Requires Ex. 6-20 insert into all_personattrs values(1,1111,'John','abc'); insert into all_personattrs values(2,2222,'Jack','def'); insert into all_personattrs values(3,3333,'James','ghi'); insert into all_studentattrs values(2222,100,'CS'); insert into all_employeeattrs values(3333,444,'Julia'); SELECT REF(p), VALUE(p) FROM Person_v p; OUTPUT: REF(P) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- VALUE(P)(SSN, NAME, ADDRESS) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 00004A038A00465A6E6E779EC1F25FE040578CE70A447E0000001426010001000100290000000000 090600812A00078401FE0000000B03C20C0C00000000000000000000000000000000000000 PERSON_TYP(1111, 'John', 'abc') 00004A038A00465A6E6E779EC1F25FE040578CE70A447E0000001426010001000100290000000000 090600812A00078401FE0000000B03C2222200000000000000000000000000000000000000 EMPLOYEE_TYP(3333, 'James', 'ghi', 444, 'Julia') 00004A038A00465A6E6E779EC1F25FE040578CE70A447E0000001426010001000100290000000000 REF(P) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- VALUE(P)(SSN, NAME, ADDRESS) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 090600812A00078401FE0000000B03C2171700000000000000000000000000000000000000 STUDENT_TYP(2222, 'Jack', 'def', 100, 'CS')
If you specify individual attributes of the declared type of the view in the SELECT list or do a SELECT *, again the query returns rows for the declared type of the view and any subtypes of that type, but these rows are projected over columns for the attributes of the declared type of the view, and only those columns are used. In other words, the subtypes are represented only with respect to the attributes they inherit from and share with the declared type of the view.
For example, the following query returns rows for all persons and rows for employees and students of all types, but the result uses only the columns for the attributes of person_typ—namely, name, ssn, and address. It does not show rows for attributes added in the subtypes, such as the deptid attribute of student_typ.
SELECT * FROM Person_v;
To exclude subviews from the result, use the ONLY keyword. The ONLY keyword confines the selection to the declared type of the view that you are querying:
SELECT VALUE(p) FROM ONLY(Person_v) p;
Generally, a query on a view with subviews requires only the SELECT privilege on the view being referenced and does not require any explicit privileges on subviews. For example, the following query requires only SELECT privileges on Person_v but not on any of its subviews.
SELECT * FROM Person_v;
However, a query that selects for any attributes added in subtypes but not used by the root type requires the SELECT privilege on all subviews as well. Such subtype attributes may hold sensitive information that should reasonably require additional privileges to access.
The following query, for example, requires SELECT privileges on Person_v and also on Student_v, Employee_v (and on any other subview of Person_v) because the query selects object instances and thus gets all the attributes of the subtypes.
SELECT VALUE(p) FROM Person_v p;
To simplify the process of granting SELECT privileges on an entire view hierarchy, you can use the HIERARCHY option. Specifying the HIERARCHY option when granting a user SELECT privileges on a view implicitly grants SELECT privileges on all current and future subviews of the view as well. For example:
GRANT SELECT ON Person_v TO user WITH HIERARCHY OPTION;
A query that excludes rows belonging to subviews also requires SELECT privileges on all subviews. The reason is that information about which rows belong exclusively to the most specific type of an instance may be sensitive, so the system requires SELECT privileges on subviews for queries (such as the following one) that exclude all rows from subviews.
SELECT * FROM ONLY(Person_v);