| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E26088-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E26088-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Use the ALTER ROLE statement to change the authorization needed to enable a role.
See Also:
CREATE ROLE for information on creating a role
SET ROLE for information on enabling or disabling a role for your session
You must either have been granted the role with the ADMIN OPTION or have ALTER ANY ROLE system privilege.
Before you alter a role to IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY, you must:
Revoke all grants of roles identified externally to the role and
Revoke the grant of the role from all users, roles, and PUBLIC.
The one exception to this rule is that you should not revoke the role from the user who is currently altering the role.
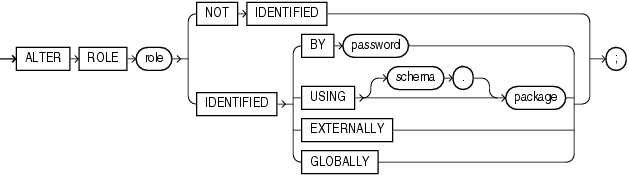
The keywords, parameters, and clauses in the ALTER ROLE statement all have the same meaning as in the CREATE ROLE statement.
Notes on Altering a Role The following notes apply when altering a role:
User sessions in which the role is already enabled are not affected.
If you change a role identified by password to an application role (with the USING package clause), then password information associated with the role is lost. Oracle Database will use the new authentication mechanism the next time the role is to be enabled.
If you have the ALTER ANY ROLE system privilege and you change a role that is IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY to IDENTIFIED BY password, IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY, or NOT IDENTIFIED, then Oracle Database grants you the altered role with the ADMIN OPTION, as it would have if you had created the role identified nonglobally.
For more information, refer to CREATE ROLE and to the examples that follow.
Changing Role Identification: Example The following statement changes the role warehouse_user (created in "Creating a Role: Example") to NOT IDENTIFIED:
ALTER ROLE warehouse_user NOT IDENTIFIED;
Changing a Role Password: Example This statement changes the password on the dw_manager role (created in "Creating a Role: Example") to data:
ALTER ROLE dw_manager IDENTIFIED BY data;
Users granted the dw_manager role must subsequently use the new password data to enable the role.
Application Roles: Example The following example changes the dw_manager role to an application role using the hr.admin package:
ALTER ROLE dw_manager IDENTIFIED USING hr.admin;