| Oracle® Database Backup and Recovery Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10643-06 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Backup and Recovery Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10643-06 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Use the GRANT command to assign privileges for a virtual private catalog schema to a database user. By default, a virtual catalog user has no access to the base recovery catalog.
Execute this command at the RMAN prompt.
A base recovery catalog must have been created with CREATE CATALOG before you can use GRANT to assign privileges for a virtual private catalog.
The best practice is to create a base recovery catalog that stores metadata for all databases. You can then create an Oracle Database user that owns the virtual private catalog schema. The virtual private catalog user must be granted the RECOVERY_CATALOG_OWNER role.
Connect RMAN to the base recovery catalog and use the GRANT command to assign recovery catalog privileges to the virtual catalog owner. Afterwards, run CREATE VIRTUAL CATALOG to create a virtual catalog schema for this user. You can use REVOKE to revoke catalog privileges.
Relationship Between Users with CATALOG Privileges on the Same Database
As an illustration of GRANT usage, suppose databases prod1 and prod2 are registered in the base recovery catalog. While logged in as SYS to the base recovery catalog, you create two virtual private catalog users: vpc1 and vpc2. You grant both users CATALOG FOR DATABASE access for database prod1, but not prod2.
In this scenario, both vpc1 and vpc2 can access the metadata for backups of prod1 made by the base recovery catalog owner. Both users can also access the metadata for backups of prod1 made by each other. Neither vpc1 nor vpc2 can access backup metadata for database prod2.
Relationship Between GRANT REGISTER and GRANT CATALOG
When you grant REGISTER DATABASE to a user, RMAN implicitly grants recovery CATALOG FOR DATABASE privileges for any database registered by this user. If you REVOKE only the REGISTER DATABASE privilege from a user (for example, virtcat), then it does not implicitly revoke the CATALOG FOR DATABASE privilege for a database registered by virtcat (for example, prod). Because the CATALOG FOR DATABASE privilege includes registration privileges for prod, virtcat can continue to unregister and register prod. To prevent virtcat from performing any operations on prod, including reregistering it, REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES from virtcat.
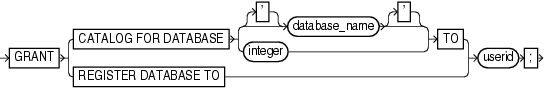
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
CATALOG FOR DATABASE[database_name | integer]TO userid |
Grants recovery catalog access for the specified database to the specified user.
Note: The catalog operations granted on the specified database include registering and unregistering this database. Specify the database by either database name or DBID. If you specify a name when multiple databases with this name are registered in the catalog, then RMAN returns an error. In this case, specify the database by DBID. To grant access to databases that are registered in the recovery catalog, you must use the |
REGISTER DATABASETO userid |
Grants the ability to for the specified user to use REGISTER DATABASE to register databases that are currently unknown to the recovery catalog.
When you grant For example, assume that user |
Example 2-89 Granting Privileges for a Virtual Private Catalog
Assume that database user rco own the base recovery catalog in database catdb. This base recovery catalog stores the RMAN metadata for a large number of databases in a data center. Your goal is to create virtual private catalogs for two backup operators in the data center.
You start SQL*Plus and connect to the catdb database as SYS. You then use the CREATE USER statement to create the bckop2 and bckop3 users on catdb. You can grant recovery catalog ownership to these users as follows:
SQL> GRANT recovery_catalog_owner TO bckop2, bckop3; SQL> EXIT
You then start the RMAN client and connect to the recovery catalog database as user rco. You use the RMAN GRANT command to give bckop2 the ability to register any database in her virtual private catalog, but grant bckop3 access to only a subset of the databases in the data center:
RMAN> CONNECT CATALOG rco@catdb
recovery catalog database Password: password
connected to recovery catalog database
RMAN> GRANT REGISTER DATABASE TO bckop2;
RMAN> GRANT CATALOG FOR DATABASE prod TO bckop3;
RMAN> GRANT CATALOG FOR DATABASE prodb TO bckop3;
RMAN> EXIT;
You start a new RMAN session and create the virtual catalog for bckop2 (sample CREATE VIRTUAL CATALOG output included). You must exit and restart RMAN after creating each virtual catalog.
RMAN> CONNECT CATALOG bckop2@catdb
recovery catalog database Password: password
connected to recovery catalog database
RMAN> CREATE VIRTUAL CATALOG;
found eligible base catalog owned by RCO
created virtual catalog against base catalog owned by RCO
RMAN> EXIT;
You start a new RMAN session and create the virtual catalog for bckop3 (sample CREATE VIRTUAL CATALOG output included):
RMAN> CONNECT CATALOG bckop3@catdb
recovery catalog database Password: password
connected to recovery catalog database
RMAN> CREATE VIRTUAL CATALOG;
found eligible base catalog owned by RCO
created virtual catalog against base catalog owned by RCO
RMAN> EXIT;
In the following example, backup operator dba1 uses her virtual private catalog, which is stored in the bckop3 schema on catdb, to store the metadata for a backup of a target database:
RMAN> CONNECT TARGET /
RMAN> CONNECT CATALOG bckop3@catdb
recovery catalog database Password: password
connected to recovery catalog database
RMAN> BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;