| Oracle® Database Backup and Recovery Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10643-06 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Backup and Recovery Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10643-06 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Use the ADVISE FAILURE command to display repair options for the specified failures. This command prints a summary of the failures identified by the Data Recovery Advisor and implicitly closes all open failures that are fixed.
The recommended workflow is to run the following commands in an RMAN session: LIST FAILURE to display failures, ADVISE FAILURE to display repair options, and REPAIR FAILURE to fix the failures.
RMAN must be connected to a target database. See the CONNECT and RMAN commands to learn how to connect to a database as TARGET.
The target database instance must be started. The target database must be a single-instance database and must not be a physical standby database, although it can be a logical standby database.
In the current release, Data Recovery Advisor only supports single-instance databases. Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) databases are not supported.
Data Recovery Advisor verifies repair feasibility before proposing a repair strategy. For example, Data Recovery Advisor checks that all backups and archived redo log files needed for media recovery are available. The ADVISE FAILURE output indicates the repair strategy that Data Recovery Advisor considers optimal for a given set of failures. The ADVISE FAILURE command can generate both manual and automated repair options.
Manual repair options are either mandatory or optional. The optional actions may fix the failures more quickly or easily than automated repairs. For example, Data Recovery Advisor may recommend a failover to a standby database as an alternative to a primary database repair.
In other cases, the only options are manual because automated repairs are not feasible. For example, I/O failures often cannot be repaired automatically. Also, it is sometimes impossible to diagnose a failure because insufficient data is returned by the operating system or the disk subsystem.
Each automated repair option is either a single repair or a set of repair steps (see Table 2-1, "Automated Repair Options" for a description of command output). When a repair option has a script that contains multiple repair steps, ADVISE FAILURE generates the script so that the repair steps are in the correct order. A single repair always fixes critical failures together. You must repair critical failures, but you can also repair noncritical failures at the same time. You can repair noncritical failures in a random order, one by one, or in groups.
Oracle RAC and Data Recovery Advisor
If a data failure brings down all instances of an Oracle RAC database, then you can mount the database in single-instance mode and use Data Recovery Advisor to detect and repair control file, SYSTEM data file, and dictionary failures. You can also initiate health checks to test other database components for data failures. This approach does not detect data failures that are local to other cluster instances, for example, an inaccessible data file.
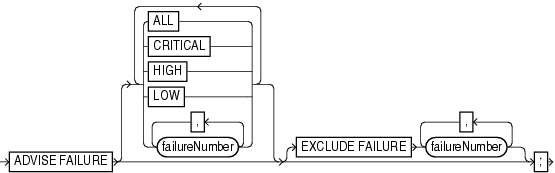
advise::=
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
ADVISE FAILURE |
Displays information for all CRITICAL and HIGH priority failures recorded in the automatic diagnostic repository.
You can only use Note: If a new failure has been recorded in the diagnostic repository since the last |
ALL |
Lists options that repair all open failures together. |
CRITICAL |
Lists options that repair only critical failures. |
HIGH |
Lists options that repair only failures with HIGH priority. |
LOW |
Lists options that repair only failures with LOW priority. |
failureNumber |
Lists options that repair only the specified failures. |
EXCLUDE FAILURE failureNumber |
Excludes the specified failures from the list. |
The ADVISE FAILURE output includes the LIST FAILURE output, which is described in Table 2-27, "List of Failures". See Example 2-5 for sample output.
RMAN presents mandatory and optional manual actions in an unordered list. If manual options exist, then they appear before automated options. Table 2-1 describes the output for automated repair options.
Table 2-1 Automated Repair Options
| Column | Indicates |
|---|---|
|
|
The identifier for the automated repair option. |
|
|
A strategy to fix the failure with the The Data Recovery Advisor always presents an automated repair option with no data loss when possible. Automated repair options fall into the following basic categories:
Note: The |
|
|
A description of the proposed repair. For example, the proposed repair could be to restore and recover data file 17. |
|
|
The location of an editable script with all repair actions and comments. If you do not choose an automated repair, then you can review this script and edit it for use in a manual recovery strategy. |
Example 2-5 Displaying Repair Options for All Failures
This example shows repair options for all failures known to the Recovery Data Advisor. The example indicates two failures: missing data files and a data file with corrupt blocks.
RMAN> LIST FAILURE;
List of Database Failures
=========================
Failure ID Priority Status Time Detected Summary
---------- -------- --------- ------------- -------
142 HIGH OPEN 23-APR-07 One or more non-system datafiles are missing
101 HIGH OPEN 23-APR-07 Datafile 1: '/disk1/oradata/prod/system01.dbf'
contains one or more corrupt blocks
RMAN> ADVISE FAILURE;
List of Database Failures
=========================
Failure ID Priority Status Time Detected Summary
---------- -------- --------- ------------- -------
142 HIGH OPEN 23-APR-07 One or more non-system datafiles
are missing
101 HIGH OPEN 23-APR-07 Datafile 1: '/disk1/oradata/prod/system01.dbf'
contains one or more corrupt blocks
analyzing automatic repair options; this may take some time
using channel ORA_DISK_1
analyzing automatic repair options complete
Mandatory Manual Actions
========================
no manual actions available
Optional Manual Actions
=======================
1. If file /disk1/oradata/prod/users01.dbf was unintentionally renamed or moved, restore it
Automated Repair Options
========================
Option Repair Description
------ ------------------
1 Restore and recover datafile 28; Perform block media recovery of
block 56416 in file 1
Strategy: The repair includes complete media recovery with no data loss
Repair script: /disk1/oracle/log/diag/rdbms/prod/prod/hm/reco_660500184.hm