| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E25519-05 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E25519-05 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Note:
TheCREATE LIBRARY statement is valid only on platforms that support shared libraries and dynamic linking.The CREATE LIBRARY statement creates a library, which is a schema object associated with an operating-system shared library. (For instructions for creating an operating-system shared library, or DLL, see Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide.)
You can use the name of the library schema object in the call_spec of CREATE FUNCTION or CREATE PROCEDURE statements, or when declaring a function or procedure in a package or type, so that SQL and PL/SQL can invoke third-generation-language (3GL) functions and procedures.
To create a library in your schema, you must have the CREATE LIBRARY system privilege. To create a library in another user's schema, you must have the CREATE ANY LIBRARY system privilege.
To use the library in the call_spec of a CREATE FUNCTION statement, or when declaring a function in a package or type, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the library and the CREATE FUNCTION system privilege.
To use the library in the call_spec of a CREATE PROCEDURE statement, or when declaring a procedure in a package or type, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the library and the CREATE PROCEDURE system privilege.
To execute a procedure or function defined with the call_spec (including a procedure or function defined within a package or type), you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the procedure or function (but you do not need the EXECUTE object privilege on the library).
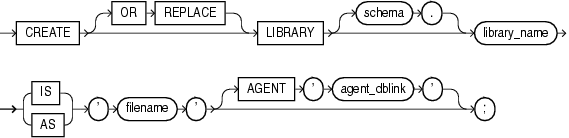
Re-creates the library if it exists, and recompiles it.
Users who were granted privileges on the library before it was redefined can still access the library without being regranted the privileges.
Name of the schema containing the library. Default: your schema.
Name that represents the library in a call_spec.
A string literal, enclosed in single quotation marks. This string should be the path or filename your operating system recognizes as naming the shared library.
The filename is not interpreted during execution of the CREATE LIBRARY statement. The existence of the library file is not checked until an attempt is made to run a routine from it.
Causes external procedures to run from a database link other than the server. Oracle Database uses the database link that agent_dblink specifies to run external procedures. If you omit this clause, then the default agent on the server (extproc) runs external procedures.
Creating a Library: Examples The following statement creates library ext_lib:
CREATE LIBRARY ext_lib AS '/OR/lib/ext_lib.so'; /
The following statement re-creates library ext_lib:
CREATE OR REPLACE LIBRARY ext_lib IS '/OR/newlib/ext_lib.so'; /
Specifying an External Procedure Agent: Example The following example creates a library app_lib and specifies that external procedures run from the public database sales.hq.example.com:
CREATE LIBRARY app_lib as '${ORACLE_HOME}/lib/app_lib.so'
AGENT 'sales.hq.example.com';
/
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about creating database links